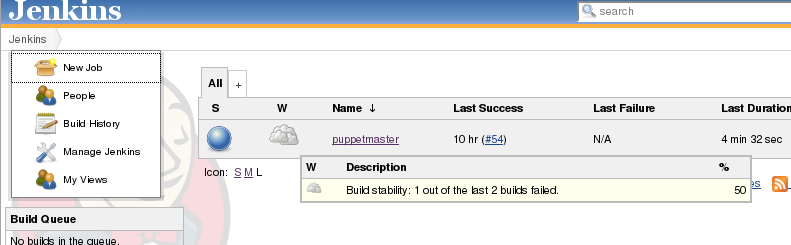
The review and project management for Git based projects is installed on a virgin Debian GNU/Linux wheezy. Developers of l2mesh must submit patchs to the git repository to gerrit:
$ git review remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (1/1) remote: Processing changes: new: 1, done To ssh://loic@gerrit.the.re:29418/l2mesh * [new branch] HEAD -> refs/publish/master/master
Gerrit is bound to jenkins : it will run tests on the patch to be reviewed and let gerrit know if it succeeds. If a developer reviews the patch positively, it can be merged into the repository.
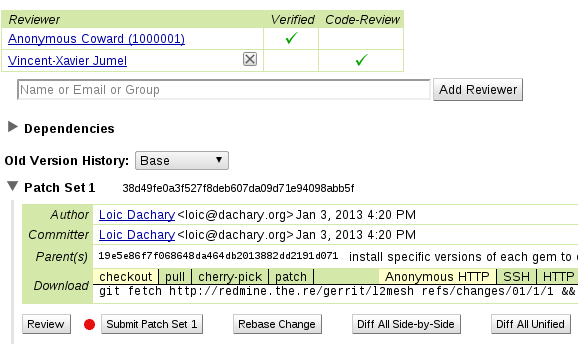
Continue reading “gerrit with jenkins : installation and configuration”